Professional Development Modules
Return to the Professional Development Module Index
Printer Friendly Version
One Plus One Makes New: Investigating Composite Materials
Grades: 5-8
Author: Joyce Brumberger
View Student Lesson Plan
Abstract
Module Description
As a result of the presenter-conducted module, participants will learn about the properties of matter and how properties can change when composite materials are produced. Through design and implementation of their own experiments, participants will design a lesson they can implement in their own classroom.
Objectives
- Participants will learn to identify properties of matter
- Participants will learn how the properties of matter can be changed
- Participants will be able to write a procedure for an experiment
- Participants will be able to analyze data and draw conclusions from that data
- Participants will produce a lesson plan to guide their own students in the design and implementation of an experiment
Materials
- Water
- Ice cubes
- Sawdust (Lowe's or Home Depot)
- Spray oil such as Pam or Baker's Joy®
- Plastic or paper 5 ounce cups
- Paper towels
- 50 mL graduated cylinders
- Containers for material disposal
- Balance scale
- Stirring stick
- Goggles
- Hammer
- C-Clamp
- Matches
- Quart size plastic containers
- 2" plastic pipe, PVC
- Meter stick or tape measure
- Watch glass
- Plumb bob with string, large weight
Procedures
Engagement
- Show an artist rendering or photograph of the Habbakuh, the proposed 2 ton pykrete aircraft carrier and tell students that it was a topic secret ship that England and the United States agreed to build during World War II. (Download from Google images.)
- Read to participants the background history of the Habbakuh at http://www.combinedops.com/Pykrete.htm
- Brainstorm together properties (characteristics, attributes) that a substance might have. (Examples: color, shine (luster), density, melting point, etc.) and write them on the board or an easel size notepad.
- Ask participants to form small groups of three or four and provide them with the materials listed in the Preparation section for Engagement.
- Tell participants to list their descriptions of the properties of the ice and sawdust on the worksheet provided. (Note: ice and sawdust may be removed from their containers) If participants request additional materials for testing determine if the request is reasonable and safe and provide materials as available.
- Ask a spokesperson from each group to share some of their observations with the whole group.
- Ask the group as a whole to brainstorm other things they might do to further determine properties of the materials. Record all responses on the board or an easel size notepad. Participants should also be recording on their worksheets.
- Ask the group to hypothesize how the properties of a material made of ice and sawdust might compare or contrast to ice itself. Record all the responses on the board or an easel size notepad.
Assessment: Assessment is on going as participants record observations and ideas as well as respond orally during the Engagement phase.
Exploration
- Ask each group to select one property they wish to explore from the large group list. Each group should be exploring a different property. The Professional Development Provider may wish to assign groups a property to expedite the process.
- Based on the property to be explored, ask each group to write a testable question so that they may test their hypothesis through experimentation. For example, if the property to be tested is melting rate, then the question might be How does the addition of sawdust frozen in water affect the melting rate of plain ice?
- Ask participants what conditions (variables) they would want to keep the same throughout their experiment so that they can insure their results were only a result of the addition of sawdust.
- Ask participants of each group to write a step-by-step, numbered procedure to test their hypothesis. An example for a procedure for melting rate might be:
- Using tongs, place the plain ice cube and the sawdust ice cube in separate plastic containers.
- Place both containers next to one another in the sun on the same surface.
- Record the initial time.
- Check containers periodically.
- Record the time when each ice block is completely melted.
- Ask groups to provide a list of all materials needed to follow their written procedures. An example of a material list might be:
- One plain ice cube
- One sawdust ice cube
- 2 quart size plastic containers
- Stopwatch
- Tongs
- Ask each group to share their procedure and, if reasonable and safe, allow them to conduct their experiment.
Assessment: The professional development provider can assess if procedures were logical and followed as written and if data was collected and recorded.
Explanation
- Ask each group to report the findings of their experiment and draw a conclusion based on those findings.
- Ask if the data supported their hypothesis.
- Ask if sufficient data was collected. If not, encourage participants to explain what they would do to collect more data.
- Discuss the variables that were kept the same and those that were changed. At this time the provider should explain the terms independent and dependent variables and provide examples of each. Participants then should be able to correctly identify the independent and dependent variables of their experiment and discuss ways they can help their students understand the terms.
- Discuss with participants how the controls of the experiment, the conditions that were kept the same, are important to identify and maintain throughout experimentation.
- Ask participants in small groups and as a large group to provide examples of controls in an experiment they might use with their students.
- Ask participants if the properties of the sawdust ice would enable a ship to be built like the proposed Habbakuh.
Assessment: Participants oral explanations of their data, analysis and conclusion will provide the professional development provider the ability to evaluate participants understanding of these aspects of experimentation. Participants' ability to provide additional examples of key terms such as dependent and independent variables, as well as experimental controls, will help the provider assess individuals' understanding of the concepts.
Elaboration
Create a durable hockey puck with water and one other common material. Test the strength of the composite material based on a procedure developed by the class as a whole. Allow each group to determine what material they want to use in the frozen water. Examples could be newspaper, cloth fibers, flour, cornstarch, etc.
- Ask participants if different amounts of the additive would affect the properties of the composite material. (Answers will vary, but experience will likely indicate that more of something might make a material stronger.)
- Tell participants they are going to make three hockey pucks with varying amounts of their material additive. The three will be: 1% additive, 5% additive, and 10% additive. This may be a time where it is necessary to talk about mass percent. If 50 mL of water is used, the mass of the water is 50 grams. To put a percentage of another material in by mass, the percent is changed to a decimal and is multiplied by the total mass. For example, if 10% of additive is to be used, the calculation would be .10 x 50 g = 5 g. In order to keep the total mass of the composite material at 50 g, 5 grams of additive would be added to 45 g of water.
- Tell participants to write a step-by-step procedure of how they are going to prepare their three test samples. Accept all reasonable procedures and allow groups to follow through with their work.
- Facilitate a group discussion to design a procedure for testing the material. Remind them about controlling variables such as the testing surface, the surface that will be hit by the puck, and the force at which the puck will be struck. An example procedure might be that the experiment will be done on the vinyl floor at a distance of 3 meters from the wall. A flat stick, like a wooden ruler or painter's stick, held in place at one end will be pulled back to a specified angle marked on the floor and released. The process will continue until signs of failure are evident (fractures or breaks).
- Have participants write the agreed procedure in their notebooks and allow the testing to begin.
- Ask participants how they are going to analyze their data. Allow them to discuss this in their group. This is the time to discuss the importance of data and graphing. A sample of data and a graph is shown below.
- NC = no change F = fracturing B = Broken
Assessment: Participants' explanations of observations vs. inferences in the participant created scenarios.
Classroom Implementation
- Have participants discuss ways that they could use observations and inferences in their classroom settings.
- Participants should complete a lesson plan template for an observation and inference lesson that addresses grade level content indicators for use in their classroom. See Lesson Plan Template handout.
- Further and on-going collaboration among participants should be encouraged.
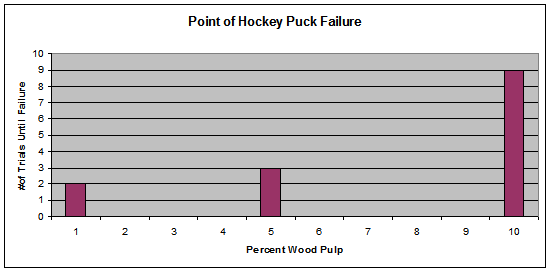
|
Trials |
Hockey Puck |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
1% |
NC |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5% |
NC |
NC |
F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10% |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
F |
|
Rationale
Understanding a historical perspective of scientific development provides a foundation upon which further advancement can be made. Working upon the success and failure of others enables a new generation of individuals to move forward in their research and development. The ideas and concepts of previous researchers can be used or adapted as new situations arise. For example, the development of pykrete in the early 1940's lead to the Habbakuk project, a floating ice aircraft carrier to be built by the United States and England. The project never came to fruition, but the concept of using ice as a matrix with other materials is used in some parts of the world today for supporting trucks and other structures.
Material science is not a new science but has been brought to the forefront in today's world with advanced technologies and increased need for new products and materials. This field of study involves the understanding of materials and their properties and examines how those properties can be altered for a desired outcome. There is a great demand for chemical, physical, and mechanical engineers in today's workforce and exposure to and application of materials such as composites in the classroom helps students develop an understanding during their pre-college years. When teachers are knowledgeable, they are better able to development awareness of future career opportunities for their students.
More detailed information on science inquiry can be found at: http://agpa.uakron.edu/k12/best_practices/
Science Standards
NSES Standard A: Science as Inquiry: As a result of activities in grades 5-8, all students should develop abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry
- Design and conduct a scientific investigation
- Develop descriptions, explanations, predictions, and models using evidence.
- Think critically and logically to make the relationships between evidence and explanations.
- Recognize and analyze alternative explanations and predictions.
- Communicate scientific procedures and explanations
NSES Standard B: Physical Science: As a result of their activities in grades 5-8, all students should develop understanding of properties and changes of properties in matter
- A substance has characteristic properties such as density, a boiling point, and solubility, all of which are independent of the amount of the sample.
NSES Standard G: History and Nature of Science: As a result of activities in grades 5-8, all students should develop understanding of Science as a human endeavor
- Science requires different abilities, depending on such factors as the field of study and type of inquiry. Science is very much a human endeavor, and the work of science relies on basic human qualities, such as reasoning, insight, energy, skills, and creativity, as well as on scientific habits of minds, such as intellectual honesty, tolerance of ambiguity, skepticism, and openness to new ideas.
NSES PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT STANDARD A: Professional development for teachers of science requires learning essential science content through the perspectives and methods of inquiry. Science learning experiences for teachers must:
- Involve teachers in actively investigating phenomena that can be studied scientifically, interpreting results, and making sense of findings consistent with currently accepted scientific understanding.
- Address issues, events, problems, or topics significant in science and of interest to participants.
- Introduce teachers to scientific literature, media, and technological resources that expand their science knowledge and their ability to access further knowledge.
- Build on the teacher's current science understanding, ability, and attitudes.
- Incorporate ongoing reflection on the process and outcomes of understanding science through inquiry.
- Encourage and support teachers in efforts to collaborate.
NSES PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT STANDARD B: Professional development for teachers of science requires integrating knowledge of science, learning, pedagogy, and students; it also requires applying that knowledge to science teaching. Learning experiences for teachers of science must:
- Connect and integrate all pertinent aspects of science and science education.
Best Teaching Practices
- Learning Cycle
- Inquiry
- Science Process Skills
Time Frame
Engagement - one 40 minute period
Exploration - two 40 minute periods
Elaboration - two 40 minute periods
Explanation - 30 minutes
Preparation
Engagement
If using paper cups, lightly spray with oil
For each group measure 50 mL of
- water and pour into a plastic cup. Freeze overnight
- sawdust and pour into a plastic cup
Fill one small quart size plastic container ¾ full of water
Elaboration:
Prepare enough ice cubes for each group to have one of each kind.
- Plain ice cubes are prepared by freezing 50 mL of water in a plastic cup overnight. 1 mL of water has a mass of 1 gram so the total mass of the water is 50 grams
- Sawdust ice cubes are prepared by freezing 7.0 grams of sawdust in 43 mL of water. The total mass is 50 grams. The sawdust is 14% of the total mass.
Safety
Water and ice can be poured down the sink.
Sawdust may be placed in a designated container for reuse. If burned, may be disposed of in another designated container, sprayed with water until cool and disposed of in the garbage.
Proper directions must be given if samples are burned or compressed.
Goggles are necessary if materials are burned or compressed.
Assessment
Assessments are ongoing throughout the learning cycle.
Teachers convert a teacher directed science activity into an inquiry-based lesson plan for their students.
Explanation of Science
Composite materials are comprised of two or more materials with different properties combined together to form a substance with new properties. The materials combine together such that they can still be identified because they have not been chemically altered. The base material is called the matrix and the added stronger material is referred to as the reinforcement. In this lesson, water was the matrix material and the wood pulp was the reinforcement. The term pykrete was given to this material in honor of Geoffrey Pyke.
Composite materials affect everyone in their daily lives and are not new ideas. Mud bricks made with another material like straw were developed thousands of years ago. Today, many composite materials are further enhanced by special manufacturing processes, which improve properties such as tensile strength or the ability to support heavier loads.
Handouts
History of Habbakuh
Properties Worksheet
Extensions
Research material science topics related to composites and industrial additives in polymeric materials.
Research the origin of the name Habbakuh.
Visit http://www.strangematterexhibit.com/properties.html and do an interactive experiment testing pykrete and concrete
Visit http://www.lbl.gov/MicroWorlds/Kevlar/index.html to do an interactive website to explore Kevlar another composite material
Research current day uses of composite materials with ice as the matrix material
Lesson Implementation Template
Download Lesson Implementation Template: Word Document or PDF File
Equity
Try to group students heterogeneously with diversity in mind.
Resources
None available for this module.
References
http://www.strangematterexhibit.com/
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=57V7HOVYuOA
http://www.combinedops.com/Pykrete.htm
http://jwgibbs.cchem.berkeley.edu/CFGoodeve/bergship.html
http://www.cabinetmagazine.org/issues/7/floatingisland.php
http://www.imechanica.org/node/1036
http://www.science.org.au/nova/059/059key.htm

